HongTide can manufacture peptides containing large range of unnatural amino acids including N-methyl amino acids, unnatural amino acids, acetyl-lysine, beta-alanine(β-Ala), aminobenzoic acid, Amidation, Acetylation, Abu, citrulline, Acm, dimethyl-Lysine, Hydroxy-proline, methyl-Lysine, mercaptopropionic acid, Nitro-Tyrosine, Norleucine (Nle), Pyro-Glutamic acid, carbobenzoxyl, succinic acid, sulfurylation etc.
{Cys(Me)}, SMC
{Ser(Me)}
{L-2-Me-Trp}
{Orn(Me)3}
{N-Me-Asp}
{N-Me-Ile}
{ADMA},{Arg(Me)2}
asymmetrical
{Lys(Me)}
{D-2-Me-Trp}
{N-Me-Gly}, Sar
{N-Me-Glu}
{N-Me-Val}
{SDMA},{Arg(Me)2}
symmetrical
{Lys(Me2)}
{Tyr(Me)}
{N-Me-Ser}
{N-Me-Ala}
{N-Me-Met}
{Arg(Me)}
{Lys(Me3)}
{Tyr(Et)}
{N-Me-Tyr}
{N-Me-Phe}
{N-Me-Nle}
{Thr(Me)}
{L-1-Me-Trp}
{D-Tyr(Et)}
{N-Me-Thr}
{N-Me-Leu}
{N-Me-Nva}
HongTide can manufacture peptides containing 20 D-amino acids including: D-Ala, D-Arg, D-Asp, D-Asn, D-Cys, D-Glu, D-Gln, D-His, D-Allo-Ile, D-Leu, D-Lys, D-Met, D-Pro, D-Phe, D-Ser, D-Tyr, D-Thr, D-Trp, D-Val.
Peptide containing D-amino acids have some advantages, such as:
1)Some peptides containing D amino acids are more biologically potent.
2)D-amino acid peptides are more resistant to proteases.
The peptide bonds formed by D-amino acids are more resistant to proteases than those formed by L-amino acids. For example, the amino-terminal Tyr-D-Ala sequence of a peptide drug is not hydrolyzed by aminopeptidases, whereas the corresponding L-peptide is degraded rapidly. Peptides can be modified using D-amino acids to ensure that they are stable against proteolysis, yet retain the same binding properties as their original all-L counterparts. Studies were performed to assess the antigenic properties and enzymatic stability of several MUC2 peptides whose residues were replaced with D-amino acids in the flanking regions.
3)D-amino acids might act as signaling molecules.
Racemase is an enzyme used by cholera bacteria to synthesize large amounts of D-methionine and D-leucine from their L-amino acid counterparts. These D-amino acids instruct cell wall-building proteins to reduce their production of peptidoglycans. The peptide isomerization reaction probably proceeds via deprotonation and reprotonation at the alpha-carbon. This reaction mechanism has been established for the racemases of several amino acids such as those of proline, aspartic acid, and glutamic acid, and two active-site cysteines are involved in this reaction. Racemases are located in the periplasmic space of a bacterium between the inner and outer membranes; it begins synthesizing D-amino acids once the cell stops growing.
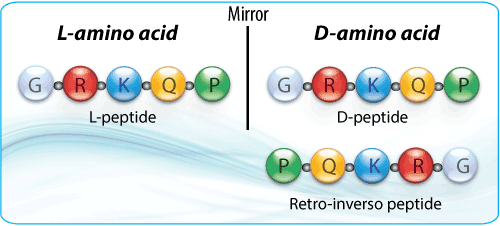
Retro-inverso peptides
Retro-inverso peptides are composed of D-amino acids that are assembled in the reverse order of their parental L-sequences. Retro-inverso peptides are obtained by replacing the normal L-amino acid residues with the corresponding D-amino acids and reversing the direction of the peptide backbone. Therefore, the original spatial orientation and the chirality of the side chains is unchanged. This results in a non-complementary side chain topochemistry between the analog and the parental L-peptide.
{Cys(Cam)}
{Cys(Nitosothiols)}
{D-Beta-Asp}
{Lys(Dde)}
{Ser(Octanoic acid)}
{Aib}
{D-Phg}
{Cit}
{D-Pen}
{Dab}
{D-Allo-Thr}
{D-Cys(Cam)}
{Cys(Pyrene-Maleimide)}
{Met(O)}
{Gly(allyl)}
{Ser(Lipoic acid)}
{Abu}
{Nva}
{D-Cit}
{Cha}
{Dap}
{Cys(Acm)}
{Gamma-Glu}
{D-Met(O)}
{D-Gly(allyl)}
{D-Ser(Octanoic acid)}
{D-Abu}
{D-Nva}
{Orn}
{D-Cha}
{Pra}
{Cys(tBu)}
{D-Gamma-Glu}
{Lys(Ac)}
{Cpg}, Cyclopentylglycine
{3-Ala(2-thienyl)-OH}
{Hyp}
{Nle}
{D-Orn}
{Chg}
{D-Pra}
{Cys(StBu)}
{Beta-Asp}
{Ac-Lys}
{Tle}
{3-Ala(3-thienyl)-OH}
{Phg}
{D-Nle}
{Pen}
{D-Chg}
{Allo-Thr}
Please contact us if the amino acids you need are not listed above.


















 Contact us by We-chat.
Contact us by We-chat.



